VOMS Admin user guide
VOMS Admin user guide
Version: 3.3.0
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Configuration
- Membership validation
- The Web Application
- Authorization
- The command line utilities
Introduction
Configuration
The recommended way of configuring VOMS and VOMS Admin is by
using the voms-configure command.
Please refer to the VOMS System administrator guide for more information about configuring the services.
Membership validation
In order to be compliant with the [JSPG policies on VO registration services][jspg-policies], VOMS Admin implements two membership validation mechanisms:
- The Acceptable Usage Policy (AUP) signature verification mechanism
- The Membership expiration mechanism
The AUP acceptance validation
The AUP acceptance mechanism enforces that every VO member has signed the VO Acceptable Usage Policy. The signature is requested at VO registration time and periodically, with the default period being every 12 months, in accordance with the EGI policy.
When the AUP signature for a user expires in the VOMS database, VOMS sends an email notification to the user requesting the signature of the AUP within a grace period.
The default AUP grace period is now 15 days after the first notification has been sent to the user that his/her signature has expired or a request to sign again the AUP has been requested by the VO administrator.
The length of the grace period can be changed using the
voms.aup.sign_aup_task_lifetime property.
When a user fails to sign the AUP in time, the user is supended, and VOMS Admin sends a notification to the suspended user and to VO administrators to inform about this fact.
Important!
No intervention is required from the VO administrator to restore the user membership. The user can restore his/her membership at anytime by signing the AUP following the link to the Sign AUP page included in the notification email.Requesting reacceptance for the VO AUP
A VO administrator can trigger the re-acceptance of the VO AUP at any time. This operation can be done for:
- a single user, by clicking the Request AUP reacceptance button in the user detailed info page.
- all VO users, by clicking the Trigger reacceptance button for the currently active AUP version.
Membership expiration validation
The membership expiration mechanism enforces that every VO member is actually
known and approved by the VO manager. When a user is registered in a VO an
expiration date is linked to his/her membership. The default lifetime for a
VOMS membership is 12 months (in accordance with the EGI policy), but can be
extended using the voms.membership.default_lifetime configuration property.
VOMS warns about expiring users in the next 30 days with an email sent to VO administrators.
The period covered by these warnings can be configured with the voms.membership.expiration_warning_period
property, to show, for instance, users about to expired in the next three months.
VOMS sends out these warning emails periodically, by default on a daily basis.
The periodicity of these warnings can be set with the voms.membership.notification_resend_period.
Once a membership expires for a given user, the user is suspended and a notification is sent to the user and the relevant VO administrators.
Important!
The user cannot extend his membership in any way. The membership can only be extended by the intervention of a VO administrator.Disabling user suspension after membership expiration
The automatic suspension of users whose membership has expired can be disabled
using the voms.preserve_expired_members configuration property. VO
Administrators will still be notified of any expired or about to expire user
in order to take action.
Turning off membership validation completely
The membership expiration checks can be completely disabled using the voms.disable_membership_end_time.
The Web Application
The VOMS-Admin web application provides a usable and intuitive interface towards VO management tasks. A screenshot of the main page of the web application is given above.

In the top part of the page, the header provides information about the current user accessing the interface and the name of the VO that is being managed. The two navigations bars provide access to the main sections of the web application.
The Home page
By clicking on the home link in the main navbar one can reach his home page.
If the current client has administrator rights, she will be directed to the admins home page. User requests for membership and group/role assignments can be managed from this page, as shown in the image below.

An administrator that is also a VO user will have a link to his user home page in the upper right part of the page.
If the current client has not admin rights, the VO user home page shows information about the user membership. From this page, the user can request group membership and role assignment and update his personal information. The page also shows information about AUP acceptance records and an history record of user’s requests.

VO members can request the addition of a new certificate to their membership by clicking on the “Request new certificate” button in the Certificates panel, as shown in the picture below:

The member can upload a PEM encoded certificate or type its certificate subject and select the CA subject from the certificate request page, pictured below:

The certificate subject should be entered following the usual /-separated openssl rendering, like in:
/C=IT/O=INFN/OU=Personal Certificate/L=CNAF/CN=Andrea Ceccanti After this step a notification is sent to the VO admin who has to approve the member’s request. The user will be informed via email of the VO admin decision on the request.
Managing users
The user management section of the VOMS-Admin web interface allows administrators to manage all the information regarding VO membership, i.e.:
- membership status
- registered certificates
- groups membership and role assignment
- generic attributes assignment
- AUP acceptance status
Suspended users
Since VOMS Admin 2.5, VOMS implements a user suspension mechanism. Suspended users are legitimate members of of the VO, but cannot obtain VOMS attribute certificates from the VOMS server.
When suspending a user a reason for the suspension must be provided by the administrator. This reason will be included in a supension notification that will be sent to the user, and shown at voms-proxy-init time to suspended users that attempt to get a VOMS proxy.
ACL Management
The ACL link the navigation bar leads to the ACL management page. The ACL management pane displays ACL entries in the form of (Voms Administrator, Set of permissions) couples. The display uses the compact representation for VOMS permissions that has been already introduced earlier.

ACL entries can be added to ACL or default ACLs by clicking on the “add entry” link. Permissions can be set for:
- VO users;
- non VO users;
- Anyone having a specific role within a specific group;
- Anyone belongin to a specific VO group;
- Any authenticated user, i.e., everyone with a certificate issued by a trusted CA
Entries added to a group ACL can be propagated to existing context’s ACLs by ticking the “Propagate to children context” tick box at the bottom of the page. Similarly, when editing or deleting an ACL entry from a group ACL, it is possible to propagate the deletion or editing to children groups by selecting the “Propagate to children context” tick box.

Managing VOMS generic attributes
Generic attributes (GAs) are (name, value) pairs that that can be assigned to VO users and that end up in the Attribute Certificate issued by VOMS. GAs extend the range of attributes that VOMS can issue besides Fully Qualified Attributes Names (FQAN), i.e., allow VOMS to issue any kind of VO membership information that can be expressed as (name, value) pairs. Such information can then be leveraged by Grid applications to take authorization decisions.
For their nature, GAs are issued to VO users. VOMS however provides a way to quickly assign GAs to all the VO members that belong to a specific VOMS group or that are assigned a specific VOMS role within a group. For this reason, you find GA management in user, group and role management pages in VOMS Admin.
To assign GA to users, the VO admin must first create the corresponding Generic Attribute class. This Generic Attribute class is used to define the name and possibly a description for the GA. VOMS Admin also implements a configurable uniqueness check on GA values that can be set when creating a GA class. This uniqueness check ensures that two users cannot share the same value for a specific GA. This check is enforced at the GA class level, so you can have GAs that are checked for uniqueness and others that allow users to share the same value for the same GA.
Generic Attribute classes management
The GA classes management page can be reached by clicking on the “Attributes” link in the navbar, and then clicking on the “Manage attribute classes” link. GA classes can then be created, specifying the GA name, description and whether uniqueness must be enforced on the GA values assigned directly to users.

Managing GAs at the user, group and role level
Once a GA class has been created, GA values can be assigned to users, groups and role within groups. As mentioned above, when one GA is assigned directly to a user, the (name,value) couple is added by VOMS to the attribute certificate returned to user. When a GA is assigned to a group, or role within a group, such (name, value) pair ends up in the Attribute Certificate of all the VO members belonging to that group (or that have such role within a group).
Search GA assignments
VOMS Admin implements search over user GA assignments, so that an administrator can easily know the status of GA assignments. The search functions deal only with GA assigned directly to user, i.e., group and role assignements search and centralized display is currently not supported.

Acceptable Usage Policies (AUP) management
Starting with version 2.5, VOMS Admin implements AUP management. AUP acceptance records are linked to each VO membership, to keep track of which version of the AUP was accepted and when.
Each AUP in VOMS Admin has a reacceptance period. Each user’s acceptance record is checked against this period and if the record has expired the user is requested to sign again the AUP.
When the user fails to sign the AUP in the allotted time, he/she is suspended.
Finally, VOMS admin provides the possibility to request re-acceptance from users at any time.
More information on AUP management and membership validation is given in the validation section.
How to disable AUP management
AUP management can be disabled by disabling the VOMS Admin registration service.
Important!
Disabling AUP management will also disable registration requests and other registration service functionality. It is currently not possible to disable only AUP management.To disable the registration service add the --disable-registration flag when configuring a VO with the voms-configure command, or put the following setting:
voms.registration.enabled = False
in the /etc/voms/VO_NAME/service.properties for a given VO. Please refer to the VOMS System administrator guide
for more information.
AUP management page

From the AUP management page is possible to add/remove new versions of the AUP, update the AUP reacceptance period, set which of the managed version is the active one (i.e., the one presented to VO users at signing time) and request reacceptance of the current version from users.
For VOMS Admin basically an AUP is the URL of a text file, so any file on the local filesystem or on a remote web server can be used for the AUP text.
Setting the VO AUP url at VO configuration time
The voms-configure –vo-aup-url option can be used to set the URL for the initial version of the VO acceptable usage policy. Please refer to the VOMS System administrator guide for more information.
If this option is not set a template vo-aup file will be created in vo runtime configuration directory /etc/voms-admin/
The Configuration Info section
The Configuration info section shows configuration information useful for voms clients, like the vomses string for the VO or a mkgridmap example configuration.

Group managers
Starting with version 3.2.0, VOMS Admin supports Group Managers. Group managers provide a way to:
- Allow the user to select which manager will be notified of their VO membership requests
- Route all group requests for a specific group to an administrator, instead of notifying all administrators that have the right to handle it
Managing group managers
Group managers can be managed by privileged administrators from the Group managers VOMS Admin web app section as shown below:
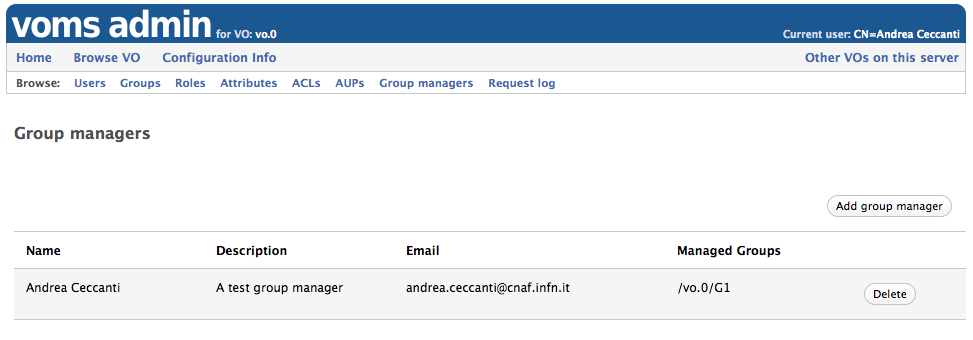
Group managers:
- can be created only when the VO is configured with more than one group
- can be linked to an existing VO group
- can manage more than one group
Important!
Group managers provides a simple notification routing mechanism which overrides the default administrator selection algorithm implemented in VOMS Admin (i.e. notify all registered administrators that would have the rights to handle a given user request).Managers are still authenticated through X.509 certificates and authorized using the VOMS ACLs, so ensure that a valid entry is present in the ACLs granting all the required permissions for each Group Manager defined.
Setting up ACLs for Group Managers
Each Group manager should have least the following permissions:
REQUEST_READ REQUEST_WRITE
on the VO root group and in the group they manage.
For more information on ACLs see the authorization section.
Group manager selection at registration time
When Group managers are defined for a VO, users can select which manager will handle their membership request.
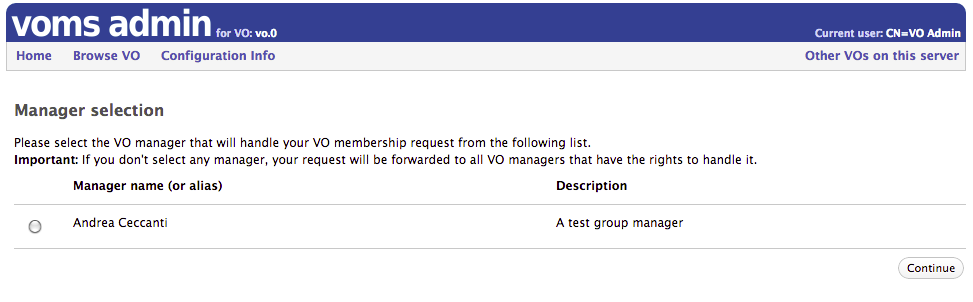
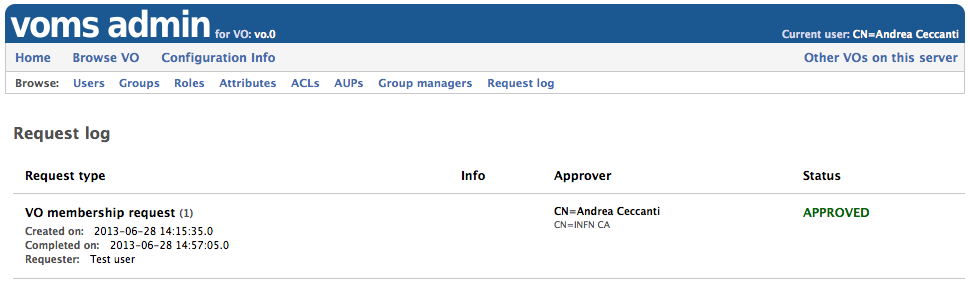
Request log
Starting with verion 3.2.0, VOMS Admin provides a request log pane, visible only by VO administrators, where details about managed requests are presented.
The Other VOs section
This section provides links to the other VOs configured on the server.
Authorization
In VOMS-Admin, each operation that access or modify the VOMS database is authorized via the VOMS-Admin Authorization framework.
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are linked to VOMS contexts to enforce authorization decisions on such contexts. A Context is either a VOMS group, or a VOMS role within a group. Each Context has a linked ACL, which is a set of access control entries (ACEs). An ACE maps a VOMS administrator to a set of permissions.
A VOMS Administrator may be:
- A VO administrator registered in the VOMS database for the VO;
- A VO user;
- A VOMS FQAN, i.e. any user who belongs to a VO group or has a given role;
- Any authenticated user (i.e., any user who presents a certificate issued by a trusted CA).
A VOMS Permission is a fixed-length sequence of permission flags that describe the set of permissions a VOMS Administrator has in a specific context. The following table explains in detail the name and meaning of these permission flags:
| Flag name | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CONTAINER_READ CONTAINER_WRITE |
These flags are used to control access to the operations that list/alter the VO internal structure (groups and roles list/creations/deletions, user creations/deletions) |
| MEMBERSHIP_READ MEMBERSHIP_WRITE |
These flags are used to control access to operations that manage/list membership in group and roles. |
| ATTRIBUTES_READ</br>ATTRIBUTES_WRITE | These flags are used to control access to operations that mange generic attributes (at the user, group, or role level). |
| ACL_READ</br>ACL_WRITE</br>ACL_DEFAULT | These flags are used to control access to operations that manage VO ACLs and default ACLs. |
| REQUESTS_READ</br>REQUESTS_WRITE | These flags are used to control access to operations that manage subscription requests regarding the VO, group membership, role assignment etc... |
| PERSONAL_INFO_READ</br>PERSONAL_INFO_WRITE | The flags are used to control access to user personal information stored in the database. |
| SUSPEND | This flag controls who can suspend other users. |
Each operation on the VOMS database is authorized according to the above set of permissions, i.e., whenever an administrator tries to execute such operation, its permissions are matched with the operation’s set of required permission in order to authorize the operation execution.
ACL inheritance and VOMS groups
Children groups, at creation time, inherit the parent’s group ACL. It is possible to change this behaviour leveraging via Default ACLs. When the Default ACL is defined for a group, children groups inherit the Default ACL defined at the parent level instead of the parent’s group ACL. So, Default ACLs are useful only if an administrator wants the ACL of children groups to be different from the one of the parent’s group.
VOMS Admin operations and required permissions
In this section, we describe the required permissions for the most comon voms-admin operations according to this notation:
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| /vo | The VO root group |
| (g,R) | The context identified by role R within group g |
| (g ➝ g') | All the voms groups that lie in the path from group g to group g' included according to the parent-child relationship defined between voms group |
| r,w,d,s | Read permission, Write permission, default permission (applies only to ACL permissions), suspend permission |
| parent(g) | Group g's parent group |
| C:, M:, Attrs:, Acl:, Req:, PI: | Container, Membership, Attributes, ACL, Requests and Personal Information permissions short names |
The table below lists operations on the left and required permissions on the right, expressed in the form of (VOMSContext, VOMSPermission) couples.